Getting Spectator View to run with your own app is obviously the most important step. How to include the required tools – including Sharing – into your app using the latest versions?
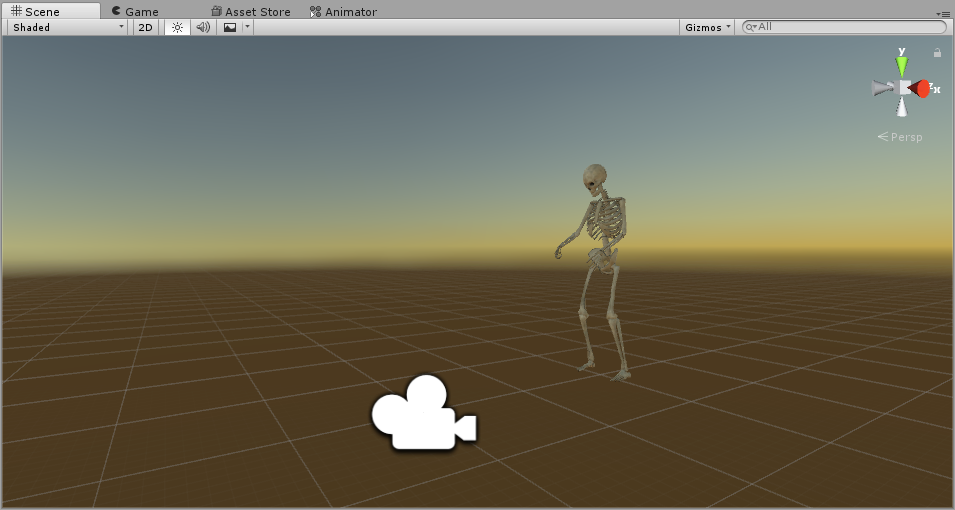
More specifically, I’ll add Spectator View to my playground project, which is mainly for placing a hologram in the room (with a few other useful scripts). Currently, this hologram is a nice, life-size skeleton from the Unity asset store.
HoloToolkit-Unity & Holographic Academy
The Holographic Academy course 240 explains how to set up your project to include Shared Holograms. It’s a good idea to work through the tutorial, as it will show you some of the basics of what is needed for Spectator View.
However, as with most of the Academy tutorials, it’s quite old. The HoloToolkit has evolved since then, and the demos often have little resemblance to what your project would look like if you start from scratch.
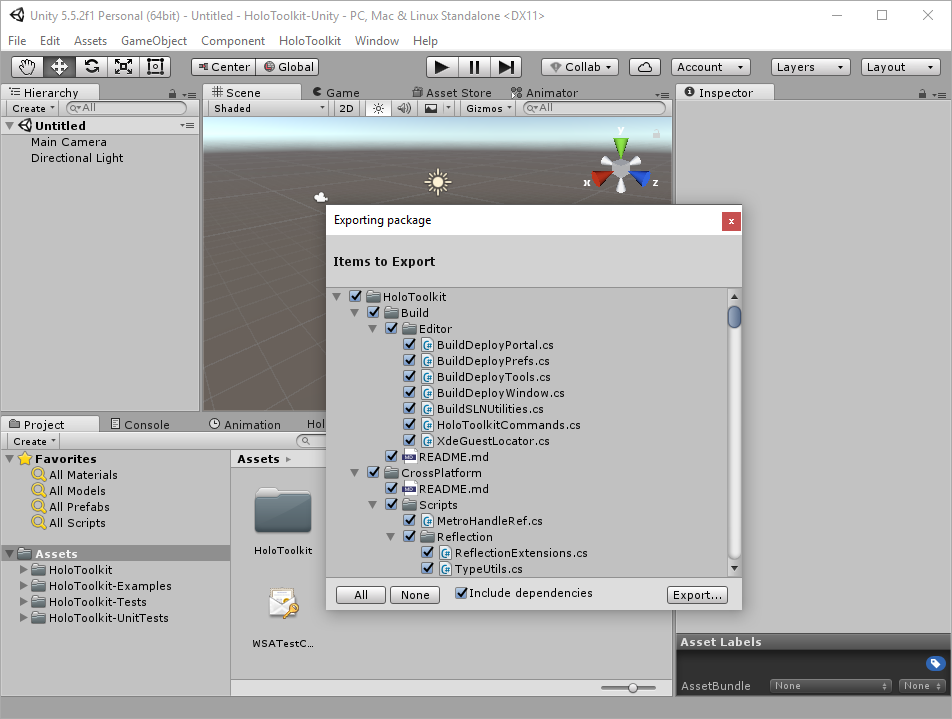
Therefore, for your own project, first clone the HoloToolkit-Unity GitHub repository to your local PC. Open the project in Unity and export the Assets folder to a new package according to the instructions.
Once this is finished, import your newly made, fresh HoloToolkit-Unity package into your own Unity project. Alternatively, you can of course use one of the pre-packaged HoloToolkit-Unity releases, which is slightly older, but is usually a good compromise.










You must be logged in to post a comment.